| Term | DEFINITION |
|---|---|
| 10BaseT | This is one of several adaptions of Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) standard for Local Area Networks(LANs). The 10Base-T standard (also called Twisted Pair Ethernet) uses a twisted-pair cable with maximum lengths of 100 meters. Cables in 10Base-T system connect with RJ-45 connectors. A star topology is common with 12 or more computers connected directly to a hub or concentrator. Also see Ethernet, LAN and RJ-45 connectors. |
| Bandwidth | The amount of data that can be transmitted in a fixed amount of time. For digital devices , the bandwidth is usually expressed in bits per second (dps) or bytes per second. For analog devices, the bandwidth is expressed in cycles per second, or Hertz (Hz). |
| Cache | A cache stores recently used information in a place where it can be accessed extremely fast. For example, a web browser like Netscape Navigator uses a cache to store on your hard drive the pages, images, sounds and URLs of web sites you visit. This means that everything doesn't have to be downloaded to your computer all over again when you visit the page again. Because accessing your computer's hard disk is much faster than accessing the internet, this speeds up web browsing significantly. |
| Data transfer rate | Alsio known as throughput, this is the speed with which data can be transmitted from one device to another. Data rates are often measured in megabits(Mbps) or megabytes (MBps) per second. DHCP Short for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, it is a protocol for assigning dynamic IP addresses to devices on a network. with dynamic addressing, a device can have a different IP address every time it connects to the network. Also see IP address. |
| DNS | This is short for Domain Name System (or Service). Every time you use a domain name, a DNS service must translate the name into corresponding IP address. For example, the domain name www.sp.edu.sg might translate to 192.168.42.129. Also see Domain Name and IP Address. <you can check the Domain Name by using NSlookup at the command prompt> |
| DOCSIS/ DOCSIS-compliant | Developed bby CableLabs and approved by ITU in march 1998, Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) defines interface standards complaint for cable modems and supporting equipment, With certification from CableLabs, manufacturers will be able to produce cable modems for retail, so consumers no longer have to depend on leased cable modems from thier cable providers. |
| Domain name | A name that identifies one or more IP address. For example, the domain name microsoft.com represents about a dozen IP addresses. Domain names are used in URLs to identify particular Web pages. For example, in the URL http://www.sp.edu.sg, the domain name is SP.EDU.SG. Also see DNS and IP address. <you can check the domain name by accessing to this website http://www.checkdomain.com/> |
| Downstream Channel |
A downsteam channle is one used to transmit signals from the headend to the user. |
| Ethernet | Ethernet is the most common type of connection computers use in a local area network (LAN). the most widely used forms of Ethernet are called 10BaseT with data transfer speeds up to 10 mbps and 100BaseT with transfer speed to 100 mbps. Also see 10BaseT and LAN |
| Hop | An intermediate connection in a string of connections linking two network devices. On the internet, for example most data packets need to go through several routers before they reach thier final destination. Each time the packet is forwarded to the next router, a hop occurs. The more hops, the longer it takes for data to go from source to destination. You can see how many hops it takes to get to another internet host by using PING or traceroute utilities. Also see Ping and Traceroute. |
| Host | A computer system that is accessed by a user working at a remote location. The system that contains the data is called the host, while the computer at which the user sits is called the remote terminal |
| Hub | A common connection point for devices in a network. Hubs are commonly used to connect segments of a LAN. A hub contains multiple ports. When a packet arrives at one port, it is copied to other ports so that all segments of the LAN can see all packets. Also see LAN |
| IMAP | Short for Interner Message Access Protocol, it is a protocol for retrieving e-mail messages. Like POP, IMAP uses SMTP for communications between the e-mail client and server. Also see POP and SMTP. |
| IP address | An identifier for a computer or device on a TCP/IP network. Networks using the TCP/IP protocol route messages based on the IP address of the destination. The format of an IP address is a 32-bit numeric address written as four number separated by periods. Each number can be zero to 255. For example 1.160.10.240 could be an IP address. Also see DHCP, DNS, Domain Name and TCP/IP |
| LAN / local | A computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or area network group of buildings. |
| MAC | Short for Media Access Control address, it is a hardware address that uniquely identifies each node of an address network. In IEEE 802 network, the Data Link Contorl(DLC) layer of the OSI Reference Model is divided into two sublayers: the Logical Link Control (LLC) layer and the Media Access Control (MAC) layer. The MAC layer interfaces directly with the network media. Consequently, each different type of network media requires a different MAC layer. Also see 10BaseT and Ethernet. |
| Newsgroup | An on-line discussion group. To view and post messages to a newsgroup, you need a newsreader, a program that runs on your computer and connects you to a news server on the internet. |
| Ping | Short for Packet Internet Groper, it is a utility to determine whether a specific IP address is accessible. It works by sending a packet to the specified address and waiting for a reply. PING is used primarily to troubleshoot internet connections. Also see IP Address and Trace route. |
| POP | Short for Post Office Protocol, it is a protocol used for email service. Also see IMAP and SMTP. |
| Proxy server | A proxy server is a server (a computer system or an application) that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or other resource available from a different server and the proxy server evaluates the request as a way to simplify and control its complexity. Today, most proxies are web proxies, facilitating access to content on the World Wide Web.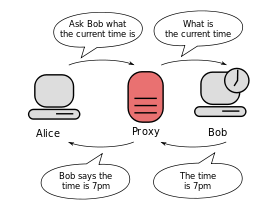 |
| RJ-45 | Short for Registered Jack-45, it is an eight-wire connector used commonly to connect computers onto a local-area network (LAN), especially Ethernets. RJ-45 connectors look similar to the ubiquitous RJ-11 connectors used for connecting telephone equipment, but they are somehwat wider. Also see 10BaseT and Ethernet. |
| SMTP | Short for Simple Mail Tranfer Protocol, It is a protocol for sending e-mail message between servers. Most email systems that send mail over the internet use SMTP to send messages form one server to another; the messages can then be retrieved with an e-mail client using either POP or IMAP. in addition, SMTP is generally used to send messages from a mail client to a mail server. This is why you need to specify both the POP or IMAP server and the SMTP server when you configure your e-mail application. Also see POP and IMAP |
| TCP/IP | Short for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, it is the suite of communications protocols used to connect hosts on the internet. TCP/IP uses several protocols, the two main ones being TCP and IP. TCP/IP is built into the UNIX operating system and is used by the internet, making it the de facto standard for transmitting data over networks. |
| Throughput | *See Data Transfer Rate |
| Traceroute | A utility that traces a packet fro your computer to an internet hotse, showing how many hops the packet requires to reach the host and how long each hop takes, if you're visiting a Web site and pages are apperaing slowly, you can use traceroute to figure out where the longest delays are occurring. Windows includes a traceroute utility called tracert. in windwos 95, you can run tracert by selecting Start->Run...cmd, and then entering tracert followed by the domian name of the host. For example: tracert www.sp.edu.sg. Also see Host and Hop |
| Upstream channel | an upstream channel is a frequency band that is used to send signal from the user to the headend. |
| USB | Short for Universal Serial Bus, it is a new external bus standard that supports data transfer rate of 12 Mbps (12million bits per second). USB also supports Pulg-and-Play installation and hot plugging. Also see Data Transfer Rate |
| UTP | Short for Unshielded Twisted Pair, a popular type of cable that consists of two unshielded wires twisted around each other. Due to its low cost, UTP cabling is used extensively for local-area network (LANs) and telephone connections. |
Don't give up when you still have something to give. Nothing is really over until the moment you stop trying
Tuesday, March 19, 2013
Glossary
The following are some common terms you might come across during this 3 year, it is used for easy reference only.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)